
“I think it is possible for ordinary people to choose to be extraordinary.” – Elon Musk
Investments can be done in multiple ways including money, time, effort, or energy.
Below are the 13 Trends to invest in Financially or with Time for astronomical returns in the second decade of 21st century
13. Human Augmentation

Human augmentation is generally used to refer to technologies that enhance human productivity or capability, or that somehow add to the human body. The field of human augmentation focuses on creating cognitive and physical improvements as an integral part of the human body
The First level of human augmentation is replication. This refers to any augmentation that replicates something a typical person can already do. You’ve likely seen examples of replication in your own life.
Take prosthetics, For example. A prosthetic leg or arm doesn’t provide the individual with an ability that most humans wouldn’t already have. It simply replicates a preexisting human function and provides it to someone who may not have had it previously.
The Second level of human augmentation is supplementation. This takes replication one step further by enabling us to do things that are already humanly possible, but better – run faster, jump higher, endure more. We’ve already seen the effects that enhancing human capabilities can have through computing.
The Third and final level of human augmentation allows humans to exceed normal abilities. Flying, for example, counts as exceeding human ability.
12. Autonomous Driving

A self-driving car, also known as an autonomous vehicle (AV), connected and autonomous vehicle (CAV), driverless car, or robotic car, is a vehicle that is capable of sensing its environment and moving safely with little or no human input
A human passenger is not required to take control of the vehicle at any time, nor is a human passenger required to be present in the vehicle at all.
Autonomous cars rely on sensors, actuators, complex algorithms, machine learning systems, and powerful processors to execute software.
Autonomous cars create a map of their surroundings based on a variety of sensors situated in different parts of the vehicle. Radar sensors monitor the position of nearby vehicles. Video cameras detect traffic lights, read road signs, track other vehicles, and look for pedestrians
When anyone talks about self-driving cars Tesla is the first thing that pops into mind. Tesla was founded in 2003 by a group of engineers who wanted to prove that people didn’t need to compromise to drive electric and that electric vehicles can be better, quicker and more fun to drive than gasoline cars. Today, Tesla builds not only all-electric vehicles but also infinitely scalable clean energy generation and storage products. Tesla believes the faster the world stops relying on fossil fuels and moves towards a zero-emission future, the better.
11. Augmented Reality, Virtual Reality and Extended Reality
Augmented reality (AR) is a view of the real, physical world in which users find elements enhanced by computer-generated input. Designers create inputs ranging from sound to video, to graphics to GPS overlays and more, in digital content that responds in real time to changes in the user’s environment, usually movement.

Augmented reality (AR) is one of the biggest technology trend right now, and it’s only going to get bigger as AR ready smartphones and other devices become more accessible around the world. AR let us see the real-life environment right in front of us for example, trees swaying in the park, dogs chasing balls, kids playing soccer. With a digital augmentation overlaid on it
Pokemon Go: Pokémon Go is one of the example of augmented reality (AR) mobile game developed and published by Niantic in collaboration with The Pokémon Company for iOS and Android devices.
Virtual Reality (VR) is the use of computer technology to create a simulated environment. Unlike traditional user interfaces, VR places the user inside an experience. Instead of viewing a screen in front of them, users are immersed and able to interact with 3D worlds. By simulating as many senses as possible, such as vision, hearing, touch, even smell, the computer is transformed into a gatekeeper to this artificial world. The only limits to near-real VR experiences are the availability of content and cheap computing power.
Virtual Reality’s most immediately-recognizable component is the head-mounted display (HMD). Human beings are visual creatures, and display technology is often the single biggest difference between immersive Virtual Reality systems and traditional user interfaces.

The virtual reality we have been referring to in this feature typically requires some form of a head-mounted display, a computer, smartphone or console that creates the 3D world and some form of input tracking, which could be hand tracking, voice or head.
virtual reality is constantly changing and improving. We’re seeing the prices of headsets falling and even the advent of new headsets being released. Technology improvements like wireless adapters and standalone VR headsets are making technology more and more accessible. As the technology improves, more game developers are getting involved too. Meaning there are more games to play and more to get excited about.
Extended Reality (XR) is an emerging umbrella term for all the immersive technologies. The ones we already have today – augmented reality (AR), virtual reality (VR), and mixed reality (MR) plus those that are still to be created.
Extended combines core features of each of them and everything between these interrelated phenomena. According to the extended reality definition, it incorporates real and virtual environments and concerns technologically powered interactions between humans and machines.
10. Hyper-automation

Hyper-automation “deals with the application of advanced technologies, including artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML), to increasingly automate processes and augment humans. Hyper-automation extends across a range of tools that can be automated, but also refers to the sophistication of the automation (i.e., discover, analyze, design, automate, measure, monitor, reassess.)”
In simple terms, hyper-automation refers to the mixture of automation technologies that exist to augment and expand human capabilities.
Hyper-automation provides business and its leaders with:
- Automated processes
- Advanced analytics
- Increased employee satisfaction and motivation
- Instant and accurate insights
- Greater productivity
Hyper-automation brings together several components of process automation, integrating tools and technologies that amplify the ability to automate work.
It starts with robotic process automation (RPA) at its core and expands automation capability with artificial intelligence (AI), process mining, analytics, and other advanced tools.
Hyper-automation can alleviate the stress on businesses in the wake of the talent shortage.
9. Digital Currency
Digital currency (digital money, electronic money or electronic currency) is a type of currency available in digital form (in contrast to physicals, such as banknotes and coins).
It exhibits properties similar to physical currencies, but can allow for instantaneous transactions and border-less transfer-of-ownership.

Digital currency is a payment method that exists only in electronic form and is not tangible. Digital currency can be transferred between entities or users with the help of technology like computers, smartphones and the internet.
Digital currencies can be used to purchase goods and services but can also be restricted to certain online communities such as gaming or social networks.
Cryptocurrency is a type of digital currency that uses cryptography to track transactions and prevent the creation of new coins by unauthorized parties.
Paper notes and coins will be obsolete and vintage in the future with the advancement of the Digital world
8. Quantum Computing
Quantum Computing is the use of quantum-mechanical phenomena such as superposition and entanglement to perform computation.
Quantum computers could spur the development of new breakthroughs in science, medications to save lives, machine learning methods to diagnose illnesses sooner, materials to make more efficient devices and structures, financial strategies to live well in retirement, and algorithms to quickly direct resources such as ambulances.

We experience the benefits of classical computing every day. However, there are challenges that today’s systems will never be able to solve. For problems above a certain size and complexity, we don’t have enough computational power on Earth to tackle them.
To stand a chance at solving some of these problems, we need a new kind of computing. Universal quantum computers leverage the quantum mechanical phenomena of superposition and entanglement to create states that scale exponentially with a number of qubits, or quantum bits.
All computing systems rely on a fundamental ability to store and manipulate information. Current computers manipulate individual bits, which store information as binary 0 and 1 states. Quantum computers leverage quantum mechanical phenomena to manipulate information. To do this, they rely on quantum bits or qubits.
There are a few different ways to create a qubit. One method uses superconductivity to create and maintain a quantum state. To work with these superconducting qubits for extended periods of time, they must be kept very cold. Any heat in the system can introduce error, which is why quantum computers operate at temperatures close to absolute zero, colder than the vacuum of space.
In order to work with qubits for extended periods of time, they must be kept very cold. Any heat in the system can introduce error, which is why quantum computers are designed to create and operate at temperatures near absolute zero.
7. Multiexperience
Multiexperience is a concept pioneered by Gartner late in 2019. The concept is being championed as one of the biggest developments for 2020. In fact, Gartner states that “more than 25% of the mobile apps, progressive web apps and conversational apps at large enterprises will be built and/or run through a multiexperience development platform” by 2023.
In short, multiexperience is about adapting to the increasing market of different devices and their respective experiences. Applications now need to run on different platforms and adapt easily, all while providing a consistent experience from a business perspective.
Multiexperience Development Platforms (mxdp)

MXDPs serve to centralize life cycle activities – designing, developing, testing, distributing, managing and analyzing – for a portfolio of multiexperience apps.
Multiexperience refers to the various permutations of modalities (e.g., touch, voice and gesture), devices and apps that users interact with on their digital journey across the various touchpoints.
Multiexperience development involves creating fit-for-purpose apps based on touch-point specific modalities, while at the same time ensuring a consistent user experience across web, mobile, wearable, conversational and immersive touchpoints.
MXDP simply means the Low Code platform integrating customized environmental experiences. The technology has gained massive traction because it comes with massive digital transformation.
6. Edge Computing
Gartner defines edge computing as “ A part of a distributed computing topology in which information processing is located close to the edge, where things and people produce or consume that information.”
Edge computing (originally coined as “fog computing” by Cisco) is an extension of the existing cloud where the smaller infrastructure components are distributed at the edge of the network.

Edge computing is a distributed computing framework that brings enterprise applications closer to data sources, such as the Internet of Things (IoT) devices or local edge servers.
This proximity to data at its source can deliver real business benefits: faster insights, improved response times and better bandwidth availability.
The basic idea there is running applications and performing related processing tasks closer to the cellular customer. This, in turn, reduces network latency and congestion, thus allowing apps to perform better.
Edge computing promises to bring storage and computing capabilities closer to mobile users, leveraging existing devices to reduce latencies and core network utilization.
5. Podcasts
In Today’s world everyone is extremely busy. You cannot always see a video to educate or Entertain yourself but plugging in earphones and listening to audio is just a casual task and it doesn’t turn many eyes in the workplace or public places. I think podcast will see growth similar to Youtube.
It will include motivational, educational audios to audio movies with 3D Experience. Of-course audio movies will need us to include the best graphic processor “Our Imagination”

A podcast is an episodic series of digital audio files that a user can download in order to listen. Alternatively, the word “podcast” may refer to the individual component of such a series or to an individual media file.
The word “podcast” is a portmanteau, a combination of the words pod and broadcast:
- Pod refers to iPod devices and implies that this content is portable so you can listen to it anywhere you go.
- Broadcast is inspired by the medium of radio as podcast content can be consumed exactly the same way.
I’m guessing that the future holds many more big players in the space, more money available to creators and better technology for listeners
I also think we are going to get better content as creators figure out more ways to monetize podcasts and as premium networks look for their next podcast stars
4. Blockchain
Blockchain applications go far beyond cryptocurrency and bitcoin. With its ability to create more transparency and fairness while also saving businesses time and money, the technology is impacting a variety of sectors in ways that range from how contracts are enforced to making government work more efficiently.
Blockchain technology enables distributed public ledgers that hold immutable data in a secure and encrypted way and ensure that transactions can never be altered.
While Bitcoin and other cryptocurrencies are the most popular examples of blockchain usage, this “distributed ledger technology” (DLT) is finding a broad range of uses. Data storage, financial transactions, real estate, asset management, and many more uses are being explored.
In the simplest terms, Blockchain can be described as a data structure that holds transactional records and while ensuring security, transparency, and decentralization.
A blockchain is a distributed ledger that is completely open to any and everyone on the network. Once a piece of information is stored on a blockchain, it is extremely difficult to change or alter it.
Blockchain owes its name to how it works and the manner in which it stores data, namely that the information is packaged into blocks, which link to form a chain with other blocks of similar information.
Application of Blockchain
Asset Management
Trade Processing and Settlement Traditional trade processes within asset management (where parties trade and manage assets) can be expensive and risky, particularly when it comes to cross-border transactions.
Insurance: Claims processing
Insurance processors have to wade through fraudulent claims, fragmented data sources, or abandoned policies for users to state a few – and process these forms manually. Room for error is huge.
The blockchain provides a perfect system for risk-free management and transparency. Its encryption properties allow insurers to capture the ownership of assets to be insured.
3. Robotics
Robotics is an interdisciplinary branch of engineering and science that includes mechanical engineering, electronic engineering, information engineering, computer science, and others.

Robotics deals with the design, construction, operation, and use of robots, as well as computer systems for their control, sensory feedback, and information processing.
The main era of robotic research and development was the mid-20th century, primarily within an industrial environment where repetitive movements and lifting of heavy objects made the use of machines over humans attractive. Robots were mainly employed for tasks that were too dirty, distant or dangerous for humans
Science-fiction author Isaac Asimov is often given credit for being the first person to use the term robotics in a short story composed in the 1940s. In the story, Asimov suggested three principles to guide the behavior of robots and smart machines.
Asimov’s Three Laws of Robotics, as they are called, have survived to the present:
- A robot may not injure a human being or, through inaction, allow a human being to come to harm.
- A robot must obey the orders given it by human beings except where such orders would conflict with the First Law.
- A robot must protect its own existence as long as such protection does not conflict with the First or Second Laws.
Life Like Robots
Robotic engineers are designing the next generation of robots to look, feel and act more human, to make it easier for us to warm up to a cold machine.
Realistic looking hair and skin with embedded sensors will allow robots to react naturally in their environment. For example, a robot that senses your touch on the shoulder and turns to greet you.
2. 3D printing
3D printing, also known as additive manufacturing, is a process by which physical objects are created by depositing materials in layers based on a digital model. All 3D printing processes require software, hardware ,and materials to work together.

3D printing technology can be used to create everything from prototypes and simple parts to highly technical final products such as Aeroplane parts, eco-friendly buildings, life-saving medical implants and even artificial organs using layers of human cells.
Methods of 3D printing
Fused filament fabrication (FFF)
Also known as fused deposition modeling (FDM). This method of 3D printing heats and extrudes plastic materials. It is common in both consumer and professional 3D printers.
Stereolithography (SLA)
This method of 3D printing uses UV light to cure or harden resins, layer by layer.
Selective laser sintering (SLS)
Common in industrial manufacturing, this method of 3D printing uses lasers to fuse powdered materials together, layer by layer.
Future of 3d Printing
Bioprinting :
when medical professionals discover a technology capable of producing customized, organic forms with some degree of precision, they decide to manufacture some human organs.
Currently, bioprinting is used to manufacture relatively simple human tissue, like cartilage or skin, and mostly for research purposes.
Prosthetics
Many professionals already use this technology to produce durable, customized parts, and prosthetics are a great example of such an application. Not only is production quick, but the designs can also be easily shared and tweaked to provide the best value to patients
Architecture and Construction
Architects periodically produce scale models to communicate their visions to colleagues and clients, and 3D printing is a prime technology for this use case. There’s no doubt that, as technology becomes cheaper and more common, the benefits that 3D printing brings to the architectural modeling process will only increase.
1. Artificial Intelligence
Artificial intelligence (AI) refers to the simulation of human intelligence in machines that are programmed to think like humans and mimic their actions.
The term may also be applied to any machine that exhibits traits associated with a human mind such as learning and problem-solving.
Artificial intelligence is based on the principle that human intelligence can be defined in a way that a machine can easily mimic it and execute tasks, from the most simple to those that are even more complex. The goals of artificial intelligence include learning, reasoning, and perception.
Turing’s paper “Computing Machinery and Intelligence” (1950), and it’s subsequent Turing Test, established the fundamental goal and vision of artificial intelligence.
Applications of AI
Gaming
Artificial intelligence in video games is largely used to determine the behavior of non-player characters (NPCs) in games. There is a tremendous increase in the use of AI in Gaming industries. A lot of AI in game development goes toward defining the way a computer opponent behaves. Behavior can range from relatively simple patterns in action games all the way to chess programs that can beat champion human players
Natural Language Processing
NLP is a field of Artificial Intelligence that gives the machines the ability to read, understand and derive meaning from human languages.
Chatbot
A chatbot is artificial intelligence (AI) software that can simulate a conversation (or a chat) with a user in natural language through messaging applications, websites, mobile apps or through the telephone.
Intelligent Robots
Intelligent robots have a range of sensors attached to them as well as their own powerful on board processors, and significant memory capacity. All of which enables them to reproduce the capacities of the human senses.
Sophia is a social humanoid robot developed by Hong Kong based company Hanson Robotics. Sophia has been covered by media around the globe and has participated in many high-profile interviews.
In October 2017, Sophia became a Saudi Arabian citizen, the first robot to receive citizenship in any country. Sophia was activated on February 14, 2016.
Machine Learning
Machine learning is an application of artificial intelligence (AI) that provides systems the ability to automatically learn and improve from experience without being explicitly programmed.
Machine learning focuses on the development of computer programs that can access data and use it to learn for themselves.
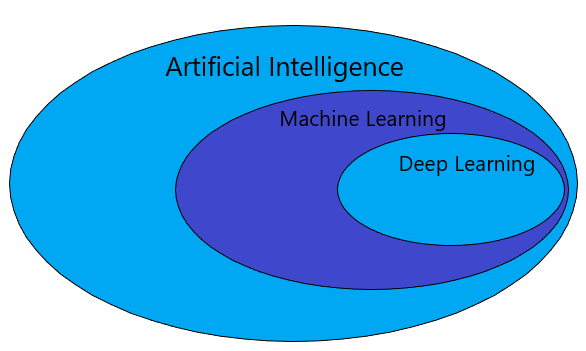
Machine Learning is the field of study that gives computers the capability to learn without being explicitly programmed. ML is one of the most exciting technologies that one would have ever come across.
As it is evident from the name, it gives the computer that makes it more similar to humans: The ability to learn. Machine learning is actively being used today, perhaps in many more places than one would expect
Deep Leaning
Deep Learning is a subfield of machine learning concerned with algorithms inspired by the structure and function of the brain called artificial neural networks.
Andrew Ng from Coursera and Chief Scientist at Baidu Research formally founded Google Brain that eventually resulted in the productization of deep learning technologies across a large number of Google services.
It is a field that is based on learning and improving on its own by examining computer algorithms. While machine learning uses simpler concepts, deep learning works with artificial neural networks, which are designed to imitate how humans think and learn.
Until recently, neural networks were limited by computing power and thus were limited in complexity.
In All, Each Trend mentioned above is going to see a Massive growth. Investing in such trends either Financially or Educationally will provide huge returns