Distance metric are used to represent distances between any two data points. There are many distance metrics, but in this article, we will only be discussing a few widely used distance metrics.
If you are new to machine learning check out : Introduction to machine learning
Type of Distances:
- Manhattan distance
- Euclidean distance
- Minkowski distance
- Hamming distance
- Mahalanobis distance
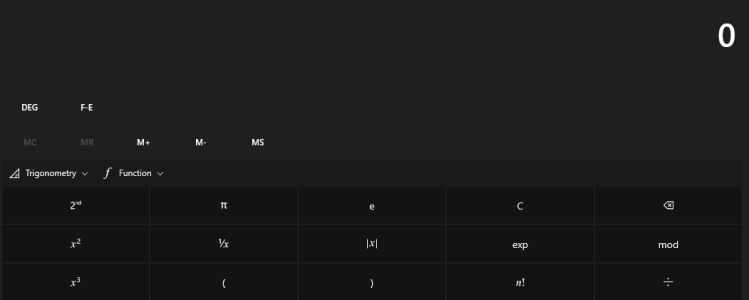
Manhattan Distance
The Manhattan distance as the sum of absolute differences
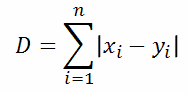
In a plane with p1 at (x1, y1) and p2 at (x2, y2), it is |x1 – x2| + |y1 – y2|.
Example:
Lets calculate Distance between { 2, 3 } from { 3, 5 }
we put it in formula
|2-3|+|3-5| = |-1| + |-2| = 1+2 = 3
In 3-D space Manhattan Distance example: [{a, b, c}, {x, y, z}] :
Abs [a − x] + Abs [b − y] + Abs [c − z]
Euclidean distance
The Euclidean distance between two points in either the plane or 3-dimensional space measures the length of a segment connecting the two points.
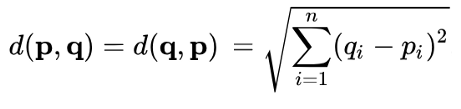
Example:
Lets calculate Distance between { 2, 3 } from { 3, 5 }
we put it in formula
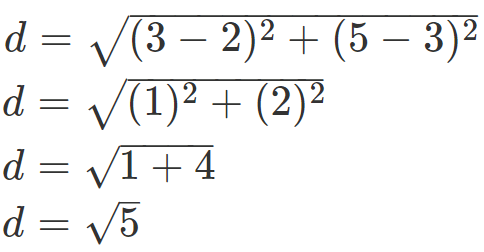
Minkowski distance
Minkowski distance is a generalization of the Euclidean distance and the Manhattan distance. Minkowski distance is applied in machine learning to find out distance similarity.
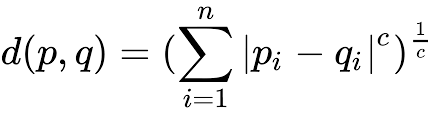
If C = 1 it is Manhattan Distance.
If C = 2 It is Euclidean distance.
Hamming distance
Hamming distance is a metric for comparing two binary data strings.
If ‘p’ and ‘q’ are binary strings then hamming distance is the number of bits required to convert from ‘p’ to ‘q’ or in other terms the number of different bits
Lets consider two binary string A = ‘010’ and B = ‘011’
Then if you change the 3 bit of string A ( 010 ) that is 0 to 1 the you get B ( 011 ) therefore the number of bits required or the number of different bits is 1 so the hamming distance for the above two string is 1 .
Mahalanobis Distance
Mahalanobis distance between two vectors, x and y, where S is the co-variance matrix.
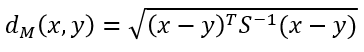
co-variance of two feature indicated how values of two features are varying together. It measure how values of one feature are varying according to values of another feature.
The Mahalanobis distance uses inverse of co-variance matrix. The ‘T’ in equation indicates transpose of a matrix.