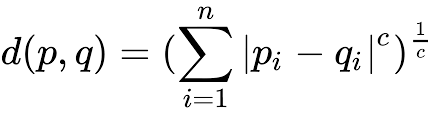” First and foremost advise, book your Exam it helps provide a boost and motivation for your studies” – YC
The International English Language Testing System, or IELTS, is an international standardized test of English language proficiency for non-native English language speakers, which is a mandatory exam if you are looking to study abroad

IELTS has been developed by some of the world’s leading language assessment experts and will test the full range of English skills needed for success in your new job or study placement abroad.
You’ll be assessed on the following elements:
- Listening
- Reading
- Writing
- Speaking
You will give Listening, Reading, Writing section on one day and the Speaking test will most probably be set 2-3 days prior of L/R/W test.
There are two IELTS tests available – IELTS Academic and IELTS General Training. The test you choose should be based on what it is you want to do.
- IELTS Academic – measures whether your level of English language proficiency is suitable for an academic environment. It reflects aspects of academic language and evaluates whether you’re ready to begin training or studying.
- IELTS General Training – measures English language proficiency in a practical, everyday context. The tasks and tests reflect both workplace and social situations.
IELTS General Training exam just differs in writing part -1, rest every other module of general and academic is the same. Writing part-1, in general, is Letter writing and in academic it is writing a summary of a graph. Both exams are only different in their difficulty level and scoring system.
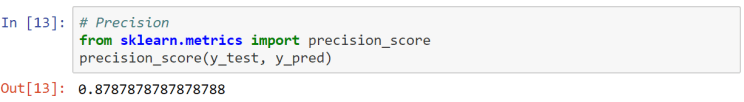
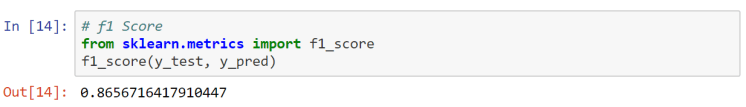
IELTS Score Calculator
All IELTS scores are between 0 and 9. You can also get .5 scores as well (for example, 6.5 or 7.5). You will get a band score for each skill ( listening, reading, writing and speaking ) and also an overall band score. The overall band score is the average score of all the skills.
- If your overall score is an average of 6.25, your score will be increased to 6.5.
- If your overall score is an average of 6.75, your score will be increased to 7.
- If your overall score is 6.1, your score will go down to 6.
- Your score is rounded up or down to the nearest 0.5 or whole score
IELTS
IELTS is not a difficult exam. I will be listing out the 4 parts and the time to be spent on the four parts.
The Writing section in IELTS is one of the difficult parts. Listening and Reading are the easiest sections to get a perfect score that is band 9. The Study material is provided below
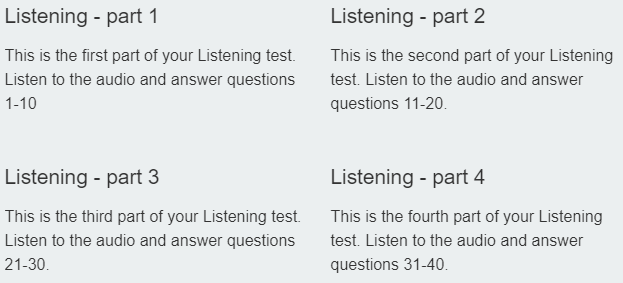
Listening
The IELTS Listening test will take about 30 minutes, and you will have an extra 10 minutes to transfer your answers to the answer sheet. Total 40 mins round
The Listening test is the same for both the IELTS Academic and IELTS General Training tests.
The four parts of this practice Listening test are presented over four separate web pages. There are 40 questions altogether. Each question carries one mark.
Listening Score chart
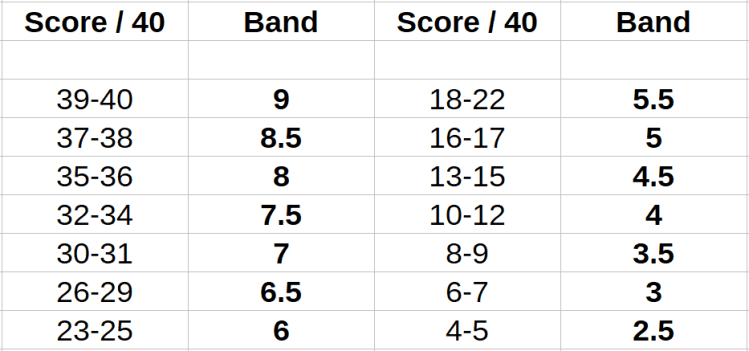
Study Material – 3 Days or 5 hours
Listening is one of the easiest modules requires less time to be spent on. You can vary the time you spend on this module but my recommendation is 3 Days. It is enough for you to do a mock test and receive a good score
You can do practice mock test on Youtube. Many Youtubes channel provide a sample listening test daily. I would suggest for you to do At least 10-12 of them it usually takes around 30 mins for each test.
You will need 3 tests just to get in the flow then 5-7 test to Practice and 3 tests for reviewing yourself.
The best way to get a band 9 in Listening is to be patient and clear your head before appearing for the test
I have provided a youtube channel link below. Videos are also categorized in their difficulty level. I would suggest Starting with Easy go to Impossible the down to hard and very hard then back to Impossible.
The IELTS Listening Test :
https://www.youtube.com/channel/UCIgELCOfrcYA9jWF4TOJUnQ/videos
Tip :
- Just remain calm and patient.
- Some time question with Fill in the black or more than two word answer might be tricky so listen carefully to them
- If there is a Map related question draw a north, south east west symbol pointing directions
- Try to forget the previous section as soon as possible
Speaking
Then Speaking section includes 3 parts. Total time required for the Speaking round will be 11-14 mins In the Speaking test, you will have a discussion with a certified examiner. It will be interactive and as close to a real-life situation as a test can get.
The Speaking test is the same for both IELTS Academic and IELTS General Training tests.
Speaking Part – 1 ( 4-5 Mins)
In part 1 of the Speaking test, the examiner will introduce him or herself and ask general questions on familiar topics. It is similar to a very short interview of Introduction. Basically, you will be asked getting to know yourself type of question
The examiner will ask you to confirm your identity. He or she will then ask general questions on familiar topics such as home, family, work, studies and interests. Part 1 of the test will last 4-5 minutes.
Speaking Part – 1 sample questions
- what kind of place is it?
- what’s the most interesting part of your town/village?
- what kind of jobs do the people in your town/village do?
- would you say it’s a good place to live? (why?)
- tell me about the kind of accommodation you live in?
- how long have you lived there?
- what do you like about living there?
- what sort of accommodation would you most like to live in?
Speaking Part – 2 ( 3-4 Mins)
In the IELTS speaking part 2 test, you will be given a task card on a particular topic, and this will include key points that you should talk about.
Part 2 is a very short speech on a topic.
- You will have 1 min to prepare yourself.
- You will have to talk for 1-2 minutes.
- Then the examiner will ask you one or two questions on the same topic.
Part 2 takes 3-4 minutes in total.
Speaking Part – 1 sample Topics
The topics given to you would also contain some pointer or hints on what to talk about. It is not necessary to stick to the points you can talk freely about the topic just keep a good flow
Example 1
Describe a piece of art you like
you can say:
- What type of art you like
- when you first saw it
- why you like it
Example 2
Describe a movie you recently saw
you can saw:
- Name of the movie
- What is it about
- What type of movie was it
- Explain if you liked it or not
Speaking Part – 3 ( 4-5 Mins)
In part 3 of the Speaking test, the examiner will ask further questions that are connected to the topics discussed in part 2.
This part of the test is designed to give you the opportunity to talk about more abstract issues and ideas. It is a two-way discussion with the examiner and will last 4-5 minutes.
It is a type of in detail interview based on the Part 2 section of speaking
Speaking Part – 1 sample Questions
Let’s consider first of all how people’s values have changed.
- What kind of things give status to people in your country?
- Have things changed since your parents’ time?
Finally, let’s talk about the role of advertising.
- Do you think advertising influences what people buy?
Study material – 3 Days 3-4 Hours
You do not require much study material for Speaking exam. When you register for IELTS you will receive a book within a few days by post depending on your location.
You will have a lot of sample questions and several topic cards in the book. That is enough for your speaking test.
The IELTS Listening Test :
https://www.youtube.com/user/AcademicEnglishHelp/videos
Tips
- show confidence in your voice
- The Examiner there will just record your voice your body language and you facially cues are not considered will marking
- Be calm do not jump to answering let the examiner finish questions first
- Pronounce clearly.
- Don’t worry if you make mistakes just keep talking
- If the questions are a bit difficult or require thinking. Say: It is an Interesting question. I have not thought about it like that give me a second to think
- Your pace is not important. your clarity is, so don’t speed up too much be clear
- You might get stuck in section 2 on the short speech here you need to think out loud. talk about it. like: I am so nervous. There are so many things to say I have difficulty picking one. Buy time for yourself by making small talk and think. Don’t make it an awkward silence
Reading
Reading is the easiest of them all. You already have the answer and questions you just need to find it.
You will be allowed 1 hour to complete all 3 sections of the IELTS Academic or General Reading test.
The three parts of this practice Reading test are presented over three separate web pages. Make sure you move swiftly from one page to the next so that your practice is as realistic as possible.
I would suggest to allocated 20 mins to each passage give or take 3-5 mins. You only have 1 hour. Time is a very important factor in this section.
Reading Score chart
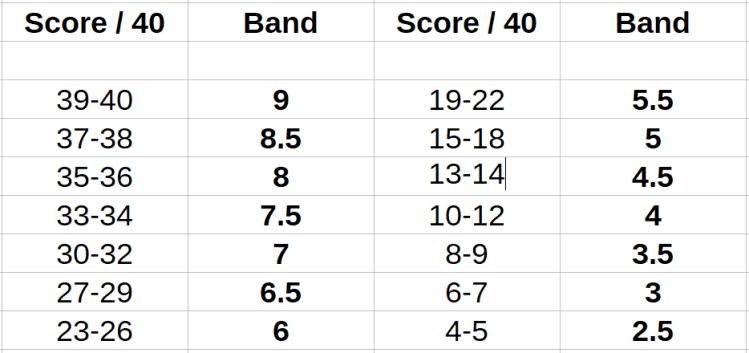
Study material – 3 Days 10-12 Hours
When you register for IELTS you will receive a book within a few days by post depending on your location.
I will describe my technique of cracking IELTS reading. I got a Band 9 in reading
I first quickly go through questions and pick out name, year, or number specified in the question and Underline them. Then I take a glance at the complete passage and get an idea of what is where while marking each and everything that looks important specifically the name and numbers. Then I try and give a name/title to the paragraph that is relevant.
Almost 90% of questions are sequential to the paragraphs. Then read one paragraph thoroughly then answers question sequentially.
Some Reading sample:
https://www.ielts-exam.net/ielts_reading/
I would suggest you to prefer the book you receive from British council. It will give you the actual feel of exam.
Tips:
- Answer questions sequentially
- Don’t waste too much time on one question if you cant answer it move to the next one
- keep a watch on time
- Try to finish each passage in 18 mins so at the end you can come back to unanswered/doubtful questions and have 6 mins to answer them
- Try to forget the previous passage as soon as you jump to the next one. Clear your mind before moving to next passage
Writing
This is the most difficult module to score a high band in, but for above average score, it is not that difficult. In this post we will only be discussing IELTS academic Writing.
The writing module is for 1 hour. I would suggest you invest 20 mins for Writing part-1 and 40 mins on Essay
There are two parts in the writing module:
Writing Part-1 (20 mins Approx.)
You need to write 3-4 paragraphs and 150+ words. If you write less than 150 words marks will be deducted
In the initial paragraph, you need to paraphrase the question. Start the paraphrase with one of the following prompts,
- The table shows/illustrates the trends in …. between …….
- The graph shows……
- The chart shows how the ….. have changed ……
I recommend you use this Structure
One Graph, Chart, or Table
Paraphrase the Prompt
Overall, Describe the main trends(Time) / Features (Things)
Compare the Data in details
Summary Sentence (Optional)
Two Graphs, Charts, or Tables
Option 1
Paraphrase the Prompt
Overall
Describe and compare the main trends(Time) / Features (Things) in Graph 1
Describe and compare the main trends(Time) / Features (Things) in Graph 2
Summary Sentence (Optional)
Option 2
Paraphrase the Prompt
Overall
Describe and compare the main trends(Time) / Features (Things) in Graph 1 and 2
Describe and compare the main trends(Time) / Features (Things) in Graph 1 and 2
Summary Sentence (Optional)
Three Graphs, Charts, or Tables
Paraphrase the Prompt
Overall
Describe and compare the main trends(Time) / Features (Things) in Chart 1
Describe and compare the main trends(Time) / Features (Things) in Chart 2
Describe and compare the main trends(Time) / Features (Things) in Chart 3
Summary Sentence (Optional)
Writing Part-1 types
- Line Graph
- Bar Chart
- Pie Chart
- Tables
- Diagram
- Maps
- Mixed Charts
Writing Part-2 Essay (40 mins Approx.)
In this part, you need to write an essay. I have search rigorously and found out this structure. You need to write 4-5 paragraphs and 250+ words. If you write less than 250 words marks will be deducted
I recommend you use this Structure
Introduction
Paragraph 1
Paragraph 2
Conclusion
Introduction Structure
Neutral background sentence
Rewrite the question
This essay will..
Paragraph Structure
Opening sentence
Supporting sentence
Evidence
Closing Sentence
Conclusion
This essay discussed …
Broad statement of Topic
Summary
Writing Part-2 types
- Problem / Solution
- Double Question
- Agree / Disagree
- Discuss Both views
- Discuss both view and give your opinion
- Advantages/ Disadvantages
- Advantages/ Disadvantages and give your opinion
Study material – 5 Days 10-15 Hours
https://www.ielts-exam.net/academic_writing_samples_task_1/
https://www.ielts-exam.net/ielts_writing_samples_task_2/
Sign up for free in E2 language. Very good training in the free module itself
https://www.e2language.com/
Tips:
- Take 1-2 mins to analyze what is given to you
- Summarize your thinking in one or two words for each paragraph and write it down
- Keep track of time
- You don’t have to write out of the box here you are tested for English, don’t waste too much time thinking
- Keep 1-2 mins at the end for checking your grammar and spellings
In All, IELTS is not a difficult exam with the study material and stuff mentioned here you can get a very good band score.